| |
Rapid, accurate and precise laboratory diagnosis is very important to help TB patients to be treated with appropriate chemotherapy. Moreover, the right information helps reduce the cost of treatment and will reduce the TB problem by helping prevent the TB epidemic, especially of drug-resistant TB.
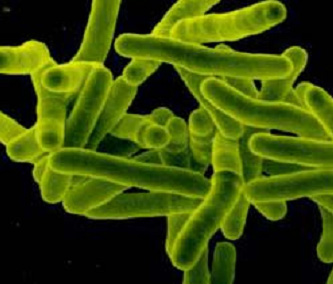
The TB germ (Mycobacterium tuberculosis) is a slow-growing bacterium. It needs 1-2 months to grow this bacteria in a culture. Approximately 5-10 % of TB infected persons develop TB disease. The target usually attacked is the lung, from which the germ can invade other organs if the infected persons have a weak immune system. Other bacteria in the Mycobacterium group can cause disease with similar symptoms as TB in people with defective immune function, especially those infected with HIV . The present method of laboratory diagnosis is based on identification of bacteria cultivated from the patient’s specimen. Although this is the most accurate identification method, it takes about 2-4 months to get the results. This affects the treatment plan. |
|